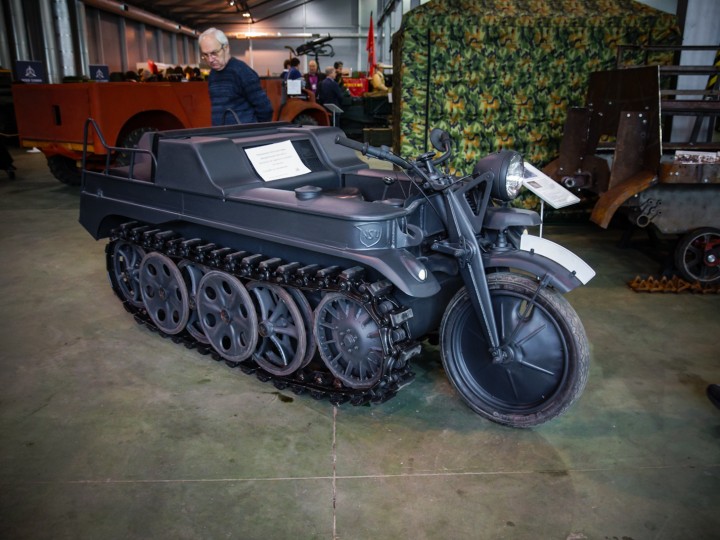
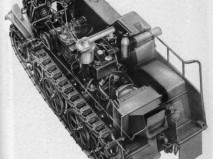
1941 NSU-Kettenkrad HK-101
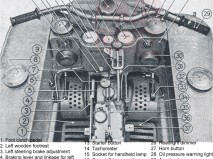
Steering the Kettenkrad was accomplished by turning the handlebars: Up to a certain point, only the front wheel would steer the vehicle. A motion of the handlebars beyond that point would engage the track brakes to help make turns sharper. It was also possible to run the vehicle without the front wheel installed and this was recommended in extreme off-road conditions where speed would be kept low.
The SdKfz 2 was designed and built by the NSU Werke AG at Neckarsulm, Germany. First designed and patented in June 1939, it was first used in the invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941. Later in the war Stoewer from Stettin also produced Kettenkrads under license, accounting for about 10% of the total production.
Most Kettenkrads saw service on the Eastern Front, where they were used to lay communication cables, pull heavy loads and carry soldiers through the deep Russian mud. Later in the war, Kettenkrads were used as runway tugs for aircraft, especially for the Me 262 jet fighters. In order to save aviation fuel, the aircraft would be towed to the runway, rather than taxiing under their own power.
The vehicle was also used in the North African theater and on the Western Front. The Kettenkrad came with a special trailer (Sd.Anh.1) that could be attached to it to improve its cargo capacity. Being a tracked vehicle, the Kettenkrad could climb up to 24° in sand and even more on hard ground, as long as the driver had the courage for it.
Only two significant sub-variations of the Kettenkrad were constructed. Production of the vehicle was stopped in 1944, at which time 8,345 had been built. After the war, production resumed at NSU. Around 550 Kettenkräder were built for agricultural use, with production ending in 1948 (some sources say 1949).